The main objective of the project is to analyze the performance of possible GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receivers that will be used in RIMS V3. Furthermore, the reaction of these receivers is analyzed when the signal transmitted by the GPS and / or Galileo satellites suffers distortions and / or anomalies. The project management is in charge of the European Space Agency (ESA).
RIMS are base stations made up of electronic equipment that have a known location on the ground and their main functionality is focused on capturing signals from satellites, obtaining data and sending them to an EGNOS subsystem.
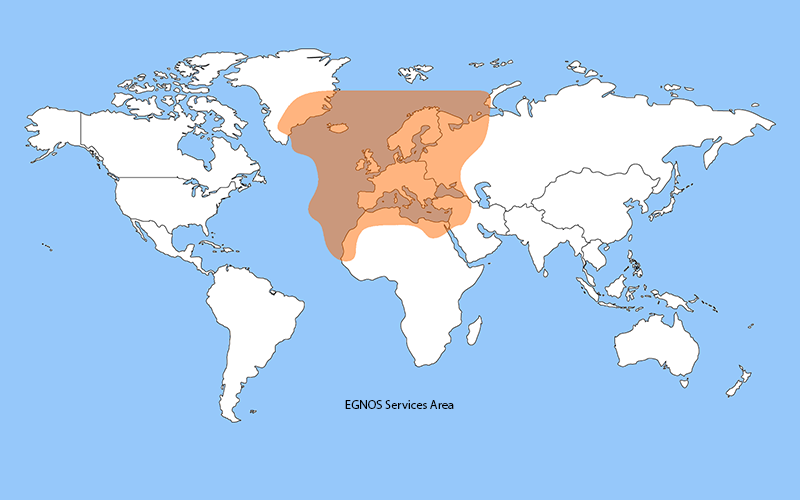
EGNOS, for its part, is the GPS augmentation system in Europe and in the future it also intends to increase the Galileo signal. It has the functionality of using geostationary satellites (GEO) that provide data for the estimation of a user's location on the earth. In this way the user can obtain a more accurate and reliable estimate of his position.
GNSS, encompasses all satellite systems (American GPS, European GALILEO, Chinese BEIDOU, Russian GLONASS), and it is a constellation of satellites that transmit signals used for positioning and location anywhere on the globe, whether on the ground. , sea or air. These allow determining the geographic coordinates and the altitude of a given point as a result of the reception of signals from constellations of artificial satellites on Earth for navigation, transportation, geodetic, hydrographic, agricultural, and other related activities.
Within our main activities there are two specifically defined actions:
1. Analyze the reaction of GNSS receivers, calculating metrics with data obtained from the GNSS receivers used in RIMS.
2. Review and support of documentation for the correct implementation of the RIMS.
GNSS receivers test:
Likewise, as part of our activities, we also participate in test campaigns for a wide variety of GNSS receivers in various scenarios such as open sky (ideal or fenced scenario with good visibility conditions) and urban (complicated scenario with poor viewing conditions). visibility).
The data obtained is used to calculate the so-called "figures of merit" by means of which the signal quality and precision of each receiver are compared in order to measure its functionality in various scenarios.
____
Technical guide:
Project type: Aerospace.
Ad Maiorem participation: design and development of GNSS systems and equipment.
Location: Noordwijk, The Netherlands.
Year: 2020.
Relevant technology:
– MALTAB
– Spirent
Regulations:
– European GNSS (Galileo) Open Service Signal-In-Space Interface Control Document.
– Interface Specification (IS-GPS-200L and S-GPS-705G).